Implants > Implants in bone deficiency
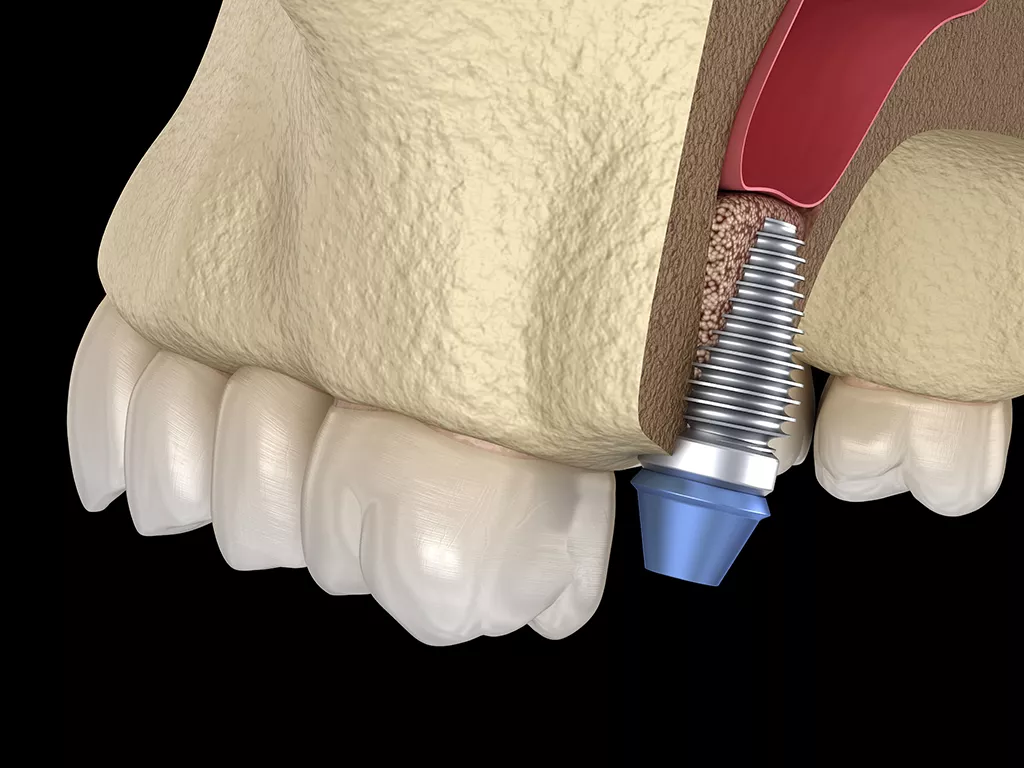
In order to place implant-supported teeth in a healthy and appropriate way, at least 1 mm of tissue is required around the implant. Therefore, bone support of sufficient width and length is needed to make long-lasting implants.
There are two basic processes used to determine the bone level:
Clinical examination by a knowledgeable and experienced physician.
3D imaging with dental volumetric tomography, where we can see all the anatomy that cannot be detected in clinical controls and even during the operation.
If it is determined that there is not enough bone in the jaw to make a healthy prosthesis, new bone can be created by applying different techniques in the lower or upper jaw, or by using the right prosthetic solution such as angled implants with the Fast & Fixed technique.
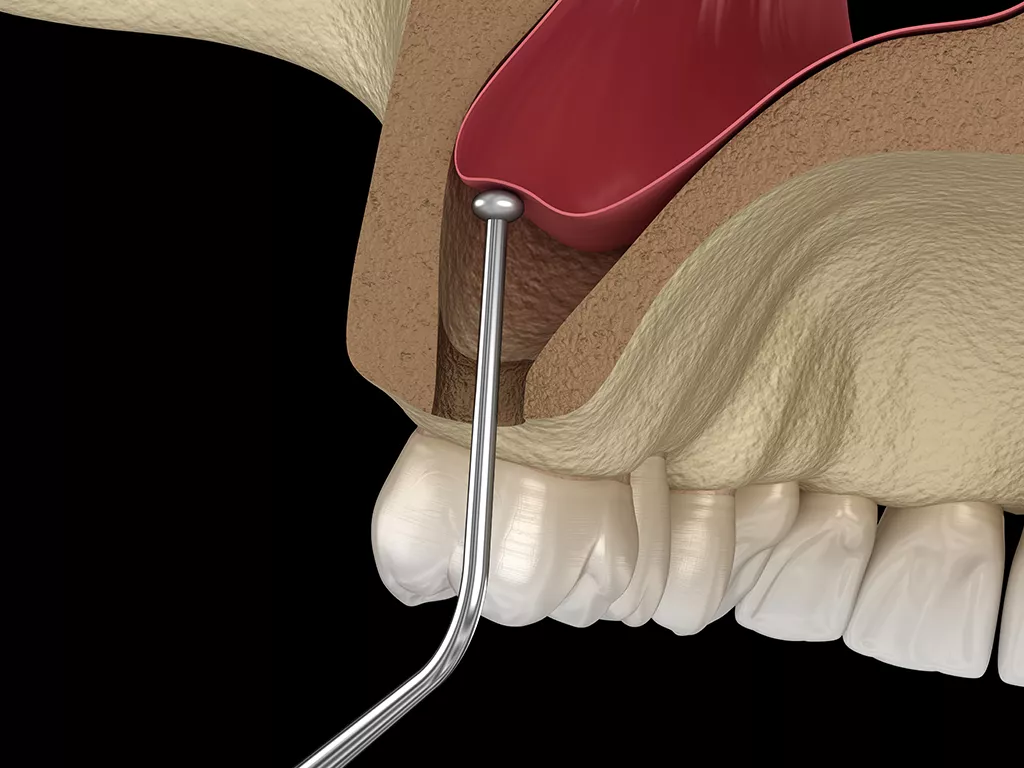

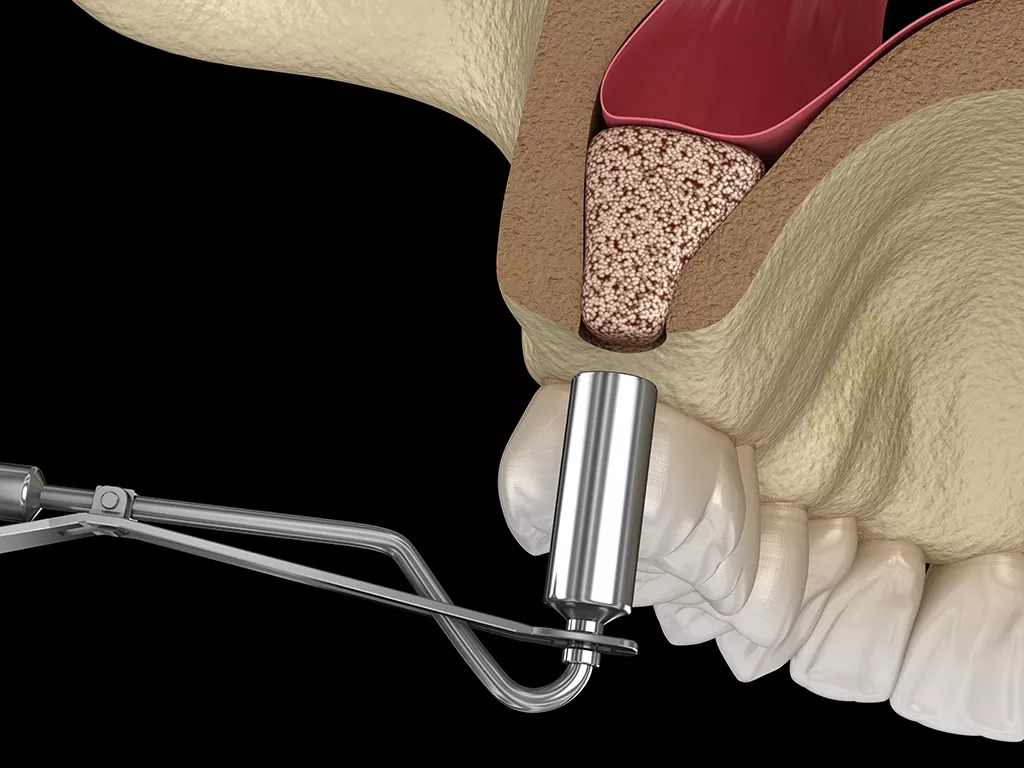

Sinuses are air spaces in the upper jaw above the posterior molars. The sinuses can cause the bone around these molars to recede overtime, making it difficult to apply the implant in this area. For this reason, sinus operations can be performed. These require a high level of accuracy and dental experience.
Using a surgical technique known as a “maxillary sinus lift,” surgeons can increase the bone thickness between the gum and the floor of the maxillary sinus.
Sinus lift operations are divided into two procedures; open lift and closed lift.
If there is not enough bone to retain the implant, the process of creating new bone formation by raising the sinus with the help of appropriate hand tools through the mouth without the need to open a side window is called closed lift. In cases where closed lift is applied, the implant procedure can be performed in the same session. Bone powder or PRF (concentrated blood containing growth cells) can be used for bone formation.
In an open lift procedure, bone formation is created by opening a window from the side wall of the sinus. If sufficient retention is provided, the implant can be applied in the same session. In cases where further retention is needed, the waiting time is often 6 months.
The main purpose of sinus surgeries is to increase the bone volume under the sinus with bone-forming materials without damaging the sinus anatomy. Thus, when the bone formation in the area matures to an adequate level, a successful implant can be applied to this area. In some cases, if there is bone in the areas adjacent to the sinus cavity, an angled implant can be placed and treated without the need for a sinus operation. If there is little bone under the sinus cavity, the need for sinus operations may be eliminated by using short implants.
It is the process of placing bone grafts (bone powders) between the jawbone and the sinus mucosa under local anaesthesia. After the operation, the bone graft fuses with natural bone over a period of 6 months. In some cases where the bone height is relatively sufficient, implants can also be made in the session where the grafts are placed.
Click on one of our members to chat on WhatsApp or send us an email at info@gloriadentravel.com
You can also call us at +34 674 224 346 during business hours.